Recently, a short video climbed up on the rank of hot topics:
A fisherman in Qingdao found a fish with a white eye in the catch. He thought the fish probably had some eye illness at the first glance. However, got the fish from net, the fisherman realized that the fish eye was embedded by a bottle cap. The fisherman was really worried that this was not the first time, sometimes indigestible plastic bags and bottles were found in fish stomach.

It is directly related to marine pollution, especially caused by waste plastics.
FROM POLLUTION TO SOLUTION: A GLOBAL ASSESSMENT OF MARINE LITTER AND PLASTIC POLLUTION latest issued by United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), evaluates the scale and severity of marine litter and plastic pollution, and reviews the solutions and action plan. It is indicated that marine litter and plastic wastes are more and more threatening in all ecosystems from the source to the ocean. Plastics are the largest, most harmful and most persistent fraction of marine litter, accounting at least 85 per cent of total marine waste.
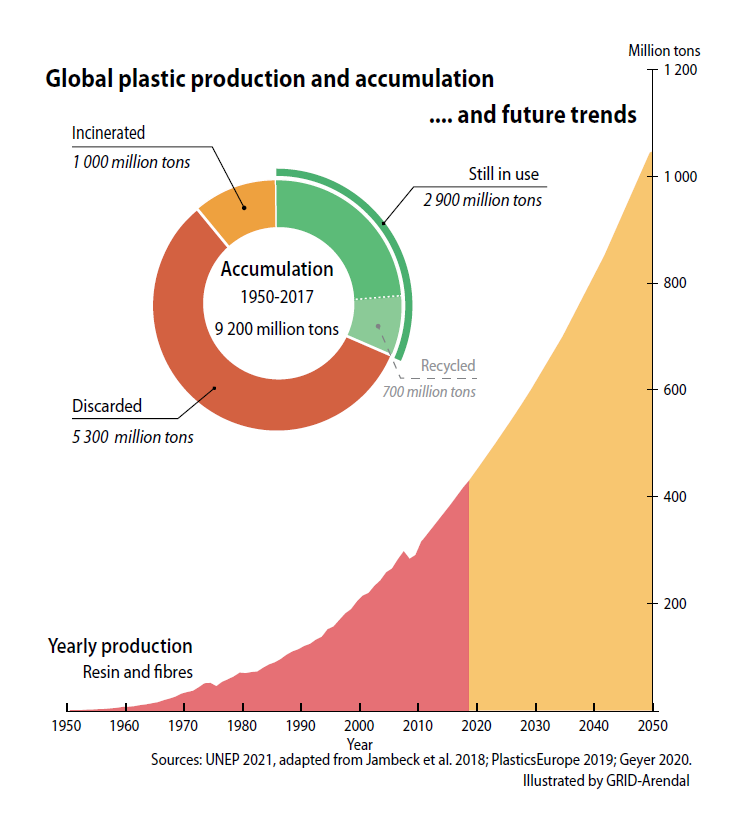
There are 9.2 billion tons of used plastics generated in the world from 1950 to 2017, in which approx. 7 billion tons finally come to plastic wastes. The recycling rate of these plastic wastes is less than 10%. Millions tons of plastic wastes are disposed in the environment, or delivered far away for incineration or landfill.
Without effective intervention, plastic wastes to marine is expected to nearly triple to 23-37 million tons per year by 2040.
Hazards of waste plastics
Plastic wastes are always threatening the environment we live on, including the oceans.
According to the life cycle assessment of plastics, the global greenhouse gas emission from plastics in 2015 was 1.7 GtCO2e. This figure is expected to increase to about 6.5 GtCO2e by 2050, accounting for 15% of the global carbon budget.
Marine litters and plastic wastes can have a significant negative impact on the natural environment and all aspects of human society.
On a biological level, both litters and plastics in the ocean pose a serious threat to marine life.
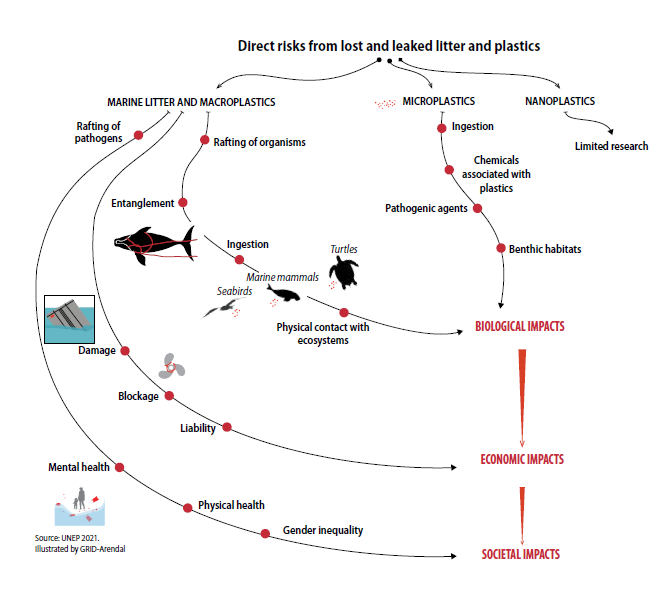
Plastic is the largest, most harmful and most persistent fraction of all marine litters. It inflicts lethal injuries to whales, seals, turtles, birds and fish, as well as invertebrates such as bivalves, plankton, worms and corals, including suffocation by wrapping around the body, tearing internal tissues, depriving of oxygen and light, causing physiological stress and poisoning.
On an ecological level, the effects of plastics on plankton and marine, freshwater and terrestrial systems also indirectly change the global carbon cycle.
Marine ecosystems, especially mangroves, sea plant, corals and salt marshes, play an important role in storing carbon. The more damage humans do to oceans and coastal areas, the harder it will be for marine ecosystems to absorb carbon emissions and withstand climate change.
On the human health level, marine litter and plastic waste also threaten human beings.
Burning plastic waste in the open air, plastic-contaminated seafood, pathogenic bacteria on plastic surfaces, and toxic and carcinogenic substances released from coastal waters can all have serious impacts on human health. Microplastics can enter the human body through breathing and skin absorption and accumulate in human organs.
On an economic level, marine litter and plastic wastes pose a serious threat to coastal communities’ sources of income, as well as to shipping and port operations.
Marine plastic waste pollution has seriously affected the global ecological environment and the survival of humans and many marine organisms. It is urgent to find a reasonable disposal method.
How to dispose the marine waste plastics?
At present, some international organizations and relevant departments in countries and regions have taken a series of countermeasures to solve the problem of marine litters, especially the problem of plastic wastes in the ocean.
WTO member countries are also taking action to support the international societies to reduce and phase out plastic products, promote ministerial dialogue and adjust trade policies to reduce plastic pollution.
In addition, a series of legislative measures, soft law measures and administrative regulations are also showing results. Among them, programs such as plastic product bans, excise taxes on plastic products, improved waste disposal technologies, economic incentives, extended producer responsibility systems, regional conventions, marine litter removal programs, educational initiatives and public awareness campaigns are being implemented on a large scale.

On the other hand, the plastics industry is advocating the use of innovative technologies that are beneficial to the environment, developing the bioplastics and alternative materials, and achieving the recycling of waste plastics in a scientific way.
Pyrolysis is effective method of waste plastic chemical recycling
Pyrolysis is based on the thermal instability of polymer such as plastics. The macromolecular organic matter is transferred into gaseous, liquid and solid components with relatively small molecular mass, through combined action of decomposition and condensation, under the oxygen-free or oxygen-deficient environment and the certain temperature conditions. Pyrolysis process realizes waste recycling to useful resources. Pyrolysis technology has advantages of low process cost, high resource level, and excellent environment benefit. It has already been the main polymer waste harmless and resource treatment technology. According to the article published in Science of The Total Environment by researchers from the University of Manchester, compared with energy recovery (burning), pyrolysis technology can reduce 50% carbon dioxide emission; compared with virgin plastic, each ton of plastic generated by chemical recycling can reduce 2.3ton carbon dioxide emission.

Through secondary use and recycling of the waste plastic products, carbon dioxide emission can be reduced to realize resource treatment, in line with the economic development model of circular economy “characterized by resource conservation and recycling, and in harmony with the environment”. It can make the waste plastics as a resource continue to be used reasonably and lastingly, and reduce the influence maximum to nature environment during plastic production and use process. Recently, there are some multinational corporations are planning to use waste plastics as an alternative to fossil fuels.
Niutech independently developed industrial continuous waste plastic pyrolysis production line completely pyrolysis process the PP PE and PS single or mixed plastics to micro molecule or monomer for generating fuel oil, solid fuel and NCG. Under the premise of safety, environmental protection, continuous and stable operation, it realizes the harmlessness and reduction recycling of waste plastics.
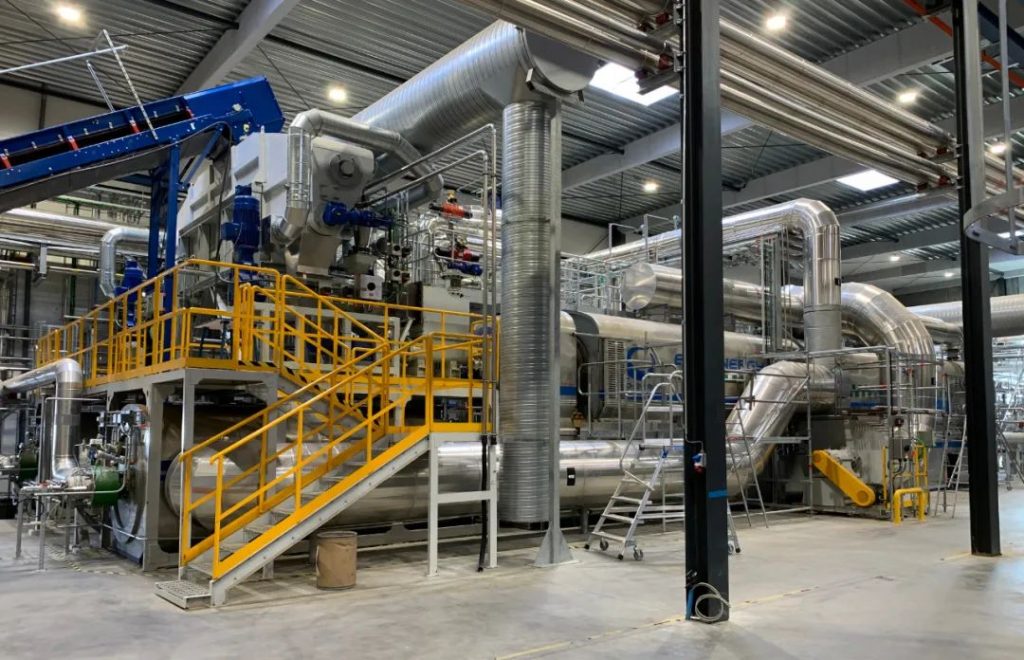

Niutech waste pyrolysis solution is used in many domestic and overseas projects successfully. Denmark waste plastic pyrolysis treatment project is recognized by global chemical giant BASF. The obtained pyrolysis outputs have been used to produce new plastics, realizing the chemical recycling from waste plastics to new plastics.
From Pollution to Solutions: A Global Assessment Report on Marine Litter and Plastic Pollution will provide information for discussion in 2022 UNEA 5.2, where the countries around the world will determine the heading direction of global cooperation. During the Fourteenth Five Year Plan, Chinese National Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Ecology and Environment also printed and distributed “14th Five-Year Plan” Action Plan for Plastic Pollution Control, which continuously promotes advanced technology and products researching application. It is imperative to promote the healthy and sustainable development of the comprehensive utilization of waste plastics industry.
Niutech will actively response to UN recall, conform to the Fourteenth Five Year Plan, based on environmental protection industry, insist on technology creation and technical researching. Niutech will provide professional solution of waste plastic chemical recycling to create a bright future.

